CASES AND PATHOLOGIES
VENTILATION MODES:
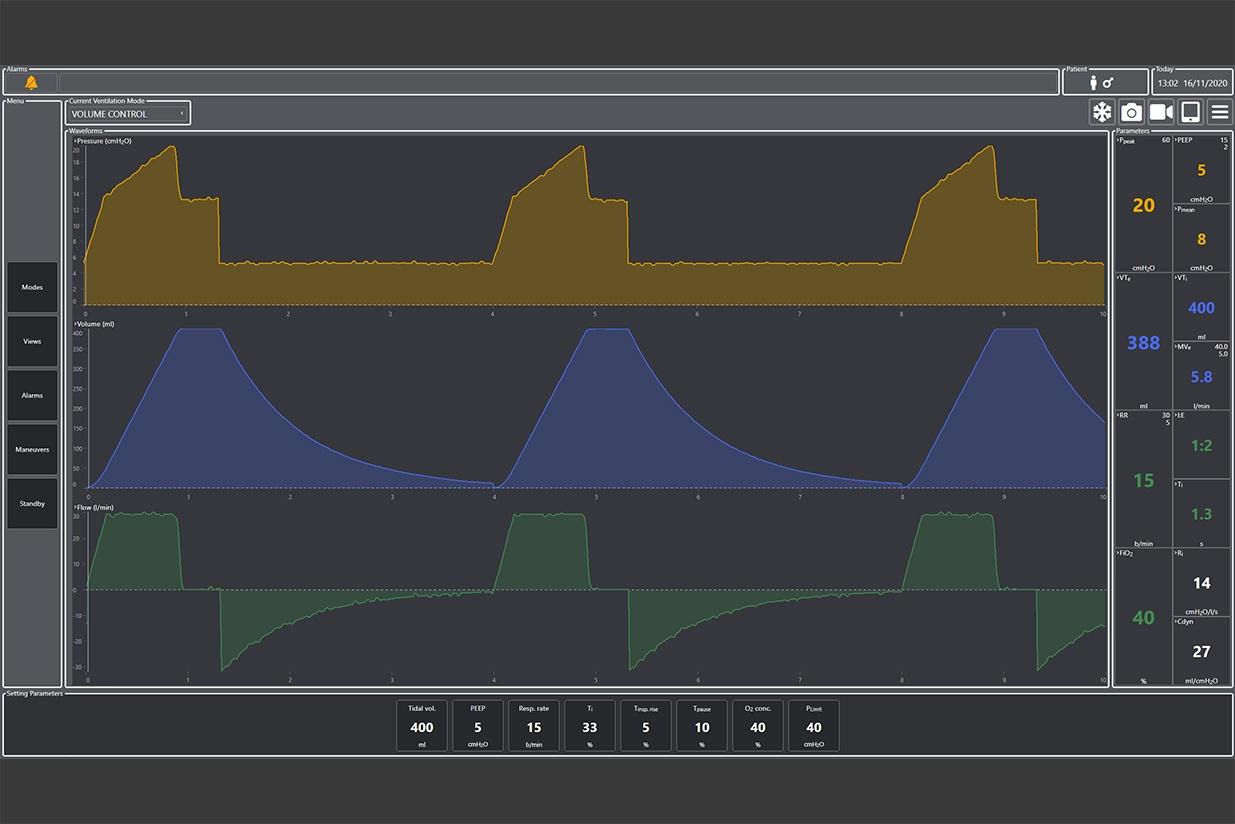
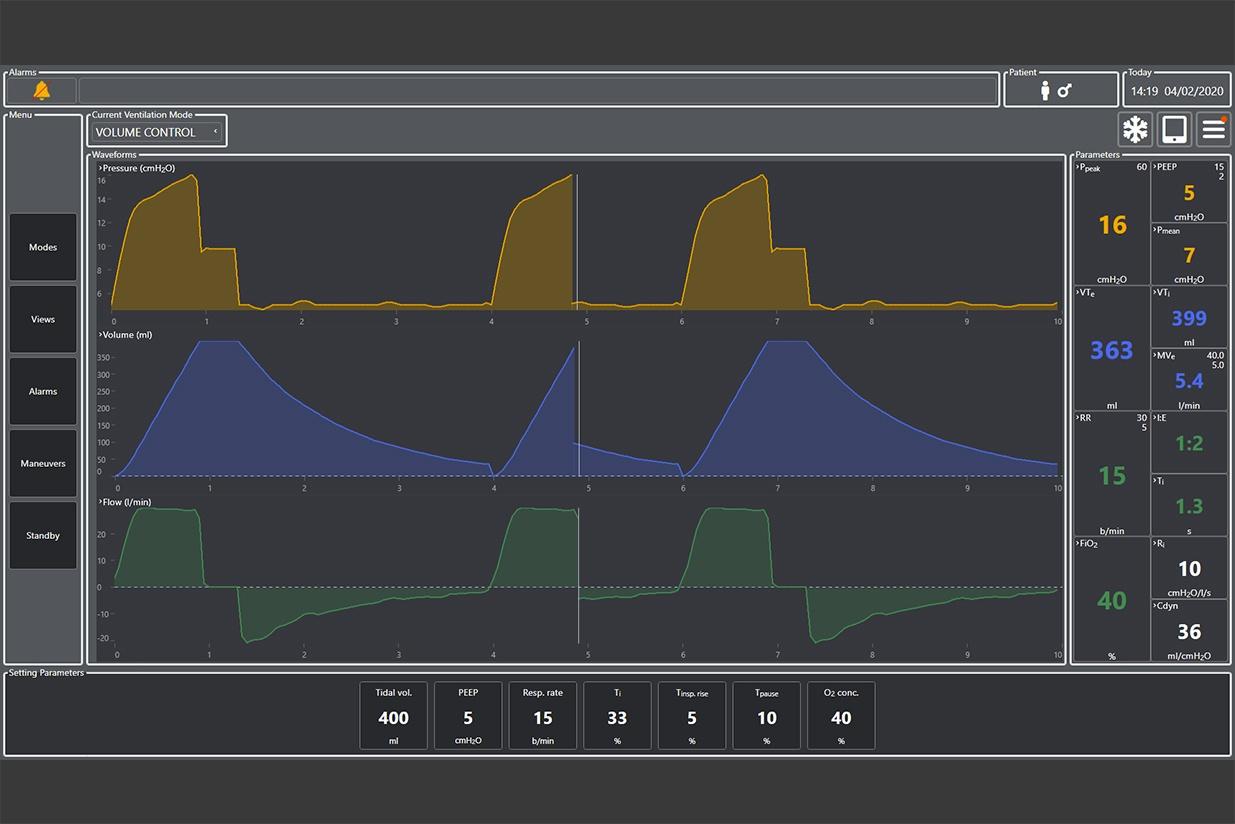
- Volume control: through this ventilation mode the user can define the tidal volume delivered to the patient. Airway pressure is the result of lung compliance, airway resistance and inspired volume.
- Pressure control: This mode of ventilation allows the user to define the inspiratory pressure delivered to the patient’s lungs.
- Pressure Assist: Using this assisted ventilation mode, which is triggered by the patient (by pressure or airflow), the user can set the ventilation simulator to provide assistance when the patient exerts respiratory effort. In this ventilation mode, the trigger threshold represents a critical setting; in fact, an incorrect value of this parameter may result in the so-called missing trigger phenomenon.
- APRV: This mode of ventilation is a form of CPAP that uses releases from the high pressure level to a low pressure level intermittently, thus allowing the delivery of inverse ratio ventilation. In this mode, the patient has the freedom to perform unassisted spontaneous breaths.
CONTROLLABLE PARAMETERS:
- The user interface also allows the user to directly change ventilation settings (such as positive end-expiratory pressure, respiratory rate or tidal volume) and to view on the virtual ventilator monitor various output parameters that are updated in real time (such as fraction of inspired oxygen, inspiratory volume per minute, etc.) and waveforms (such as pressure, volume, pressure and flow): Esp, Expiratory Minute Volume, Inspiratory Minute
- Volume, Impulse Pressure Value, the Volume – Pressure Loop, the Flow – Volume Loop, etc.).
- The instructor can change the value of parameters such as lung compliance, thoracic compliance, resistances, respiratory muscle effort that describe the patient’s characteristics and this will clearly affect the respiratory rate, inspiratory time, oxygen saturation, end tidal CO2 and blood pressure of the high fidelity simulator.